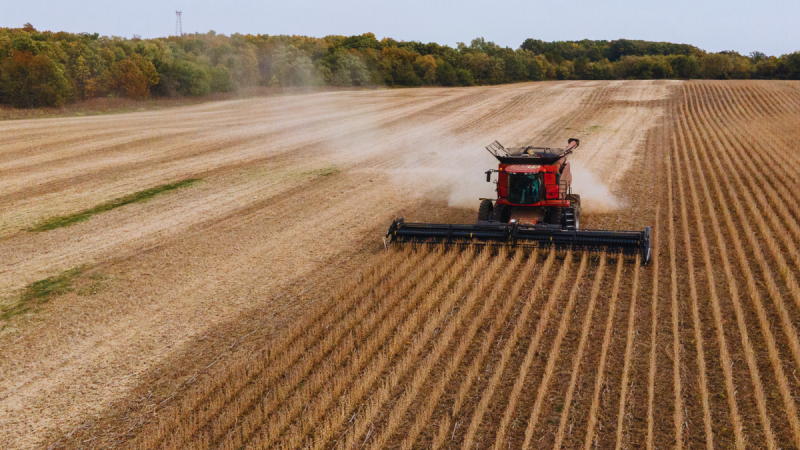
On the heels of President Donald Trump’s meeting with Chinese leader Xi Jinping, Beijing has agreed to restart its purchases of U.S. soybeans, a $30 billion cornerstone of American agriculture that was once wielded as a weapon in the battle for global trade leverage.
Once a quiet export success story, America’s humble soybean became a political flashpoint after Beijing halted imports in retaliation for Trump’s tariffs on Chinese goods. China’s shift to suppliers in Brazil and Argentina exposed how quickly global trade flows can realign and how vulnerable U.S. farmers remain to diplomatic friction.
Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said Thursday that China will buy 12 million metric tons of American soybeans during the current season through January and has committed to buying another 25 million tons annually for the next three years as part of a larger trade deal.
In an interview with Fox Business’ ‘Mornings with Maria,’ Bessent added that several Southeast Asian nations have also agreed to buy a combined 19 million tons of U.S. soybeans, though he did not specify a timeframe for those purchases.
‘So our great soybean farmers, who the Chinese used as political pawns, that’s off the table, and they should prosper in the years to come,’ Bessent said.
What began as tit-for-tat posturing between the world’s two largest economies evolved into both a symbolic and economic gut punch for Trump’s rural base, whose livelihoods depend on the very trade ties now caught in the crossfire.
According to the American Soybean Association, the U.S. has traditionally served as China’s leading soybean source. Prior to the 2018 trade conflict, roughly 28% of U.S. soybean production was exported to China. Those crop exports fell sharply to 11% in 2018 and 2019, recovered to 31% by 2021 amid pandemic-era demand and eased back to 22% in 2024.
But some policy experts argue that China’s shift away from U.S. soybeans was already underway.
‘China was always going to reduce its reliance on the United States for food security,’ Bryan Burack, a senior policy advisor for China and the Indo-Pacific at the Heritage Foundation told Fox News Digital. ‘China started signing purchase agreements with other countries for soybeans well before President Trump took office.’
He added that Beijing has ‘been decoupling from the U.S. for a long time.’
‘Unfortunately, the only way for us to respond is to do the same, and that process is painful and excruciating,’ Burack said.
But for farmers thousands of miles from Washington and Beijing, those policy shifts translate into shrinking markets and tighter margins.
‘We rely on trade with other countries, specifically China, to buy our soybeans,’ Brad Arnold, a multigenerational soybean farmer in southwestern Missouri, told FOX Business ahead of Trump’s bilateral meeting with Xi. He said China’s decision to boycott U.S. soybean purchases ‘has huge impacts on our business and our bottom line.’
‘There are domestic uses for soybeans, looking at renewable diesel, biodiesel specifically produced from soybeans,’ Arnold said.
‘In the grand scheme of things, that’s such a small percentage currently, you know it’s going to take a customer like China to buy beans to make a noticeable impact. You can’t take our No. 1 customer, shut them off and just overnight find a replacement.’
Whether China’s new purchases signal a genuine thaw in U.S.–China trade relations or just a temporary reprieve, the deal underscores how closely diplomacy and agriculture remain intertwined.
Fox Business’ Eric Revell contributed to this report.